الوصف
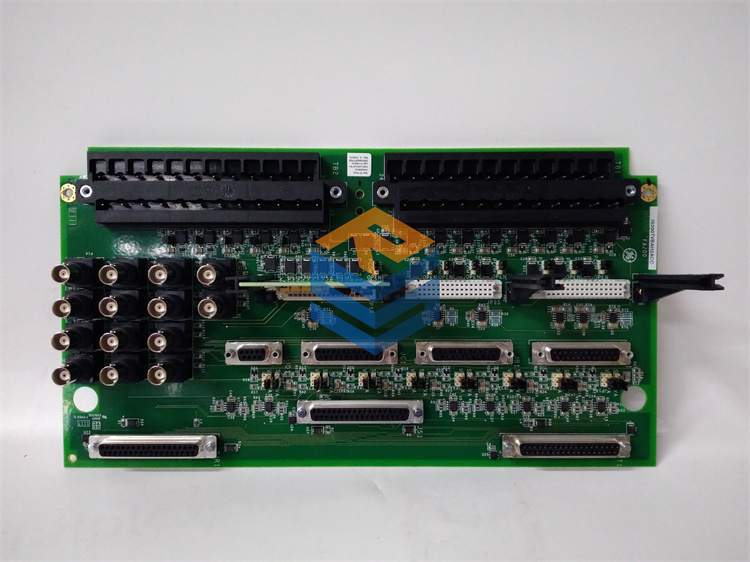
The GE part number IS200EBRGH2A is an EX2100E Gate Pulse Board. It is a crucial component of GE’s Mark VIe Excitation Control System. Its primary function is to generate and transmit the high-speed gate pulses that control the firing of the SCRs (Silicon Controlled Rectifiers) in the thyristor bridge of a generator’s exciter. ⚡
Function and Key Features
A thyristor bridge is a power electronic circuit that converts AC to DC power to supply the generator’s field. The IS200EBRGH2A board controls this process with incredible precision.
- Gate Pulse Generation: The board receives control signals from the main controller (like a DSPX) and then generates a series of timed electrical pulses called “gate pulses.” These pulses are sent to the gate terminals of the SCRs in the bridge.
- Precision Timing: The timing of these pulses is critical. By precisely controlling the firing angle of the SCRs, the board can regulate the amount of DC current flowing into the generator’s field, which in turn controls the generator’s output voltage. This is a core function of the excitation system.
- 42-77MM: The “42-77MM” in the part number likely refers to the mechanical dimensions or a specific form factor of the board, such as its width, suggesting it may fit in a narrower slot than the 100MM version.
- System Integration: The EBRG board works in conjunction with the main control card and other I/O boards to form the complete excitation control system.
- Robust Design: Like all GE industrial control components, it’s built to withstand the harsh conditions of a power plant.
Applications
The IS200EBRGH2A is a key component in power generation facilities that have upgraded to the Mark VIe Excitation Control System. It is used for:
- Excitation Control: It provides the final, high-speed control signal that directly regulates the generator’s voltage and reactive power.
- Power Regulation: By precisely controlling the power flow to the generator’s field, it ensures the generator’s output is stable and reliable, which is crucial for maintaining the stability of the electrical grid.



 +86 15340683922
+86 15340683922 +86 15340683922
+86 15340683922

