الوصف
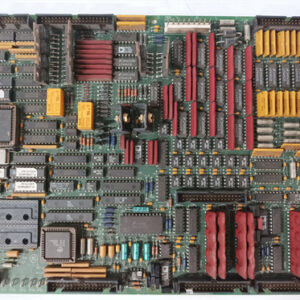
The GE IS200ISBDG1AAA is a multi-functional printed circuit board (PCB) for the Mark VI Speedtronic Turbine Control System.
While it is named the Phase Carrier Control Power Detector Board in some documentation, its functional acronym is ISBD, which stands for Insync Delay Board or ISBus Delay Module.
⚙️ Primary and Secondary Functions
The board’s functions fall into two main categories:
1. Primary Function (ISBus Delay)
As an Insync Delay Board, the primary and critical function is to introduce a precise, calculated time delay into the proprietary ISBus communication signals.
-
Synchronization (InSync): In Triple Modular Redundant (TMR) Mark VI systems, the board compensates for minute physical differences in wiring paths, ensuring that all three control modules (R, S, T) receive critical synchronization signals at the exact same moment.
-
System Integrity: This compensation is vital for maintaining the strict real-time timing required for the TMR system’s voting logic and reliable fault-tolerant operation.
2. Secondary Function (Communication and Detection)
The board is also heavily equipped to handle serial communication and power detection, which gives rise to its longer name:
-
Serial Communication: It functions as a serial communication board, providing multiple serial communication ports (often six in total) to interface the control system with external devices.
-
It typically supports multiple protocols, including RS-232C, RS-485, and RS-422 interfaces.
-
It supports full duplex communication for RS-232C and RS-422.
-
-
Phase Carrier Control Power Detection: This name suggests circuitry is present to detect or monitor control power and possibly phase carrier signals, contributing to overall system diagnostics.
-
Power Input: It includes a terminal strip (P4) labeled 24 VDC Input.
🔎 Technical Features
The board’s physical layout and components are designed to support its dual function:
-
Revision: The G1AAA suffix indicates the board belongs to Hardware Group 1, Artwork Revision A, with subsequent assembly/manufacturing revisions.
-
Connectors:
-
It features a 20-pin vertical male ribbon connector (P5).
-
Other connectors (P1-P3) are labeled for communication functions like Full Duplex, XMIT Out, and RCV In.
-
-
Components: It is built with metal film resistors, ceramic/electrolytic capacitors, two transformers, and several integrated circuits, including potentially an FPGA and oscillation chips.
-
Diagnostics: It includes Test Points (TP) and usually two LED indicator lights labeled “Fail” and “Run” (or similar status indicators) on the front panel for diagnostics.



 +86 15340683922
+86 15340683922 +86 15340683922
+86 15340683922